News & Updates

Instead of Relying on Stories, We All Need Access to Better COVID-19 Data
The potential of data lies not in its ability to reinforce stories — that leaves us reliant upon the storytellers. Instead, comprehensive and readily available data facilitate conversations that allow the broader community to see exactly what is happening and, if necessary, question assumptions about our current situation and what lies ahead. Over the last two weeks, it has become clear that state and county leadership do not have full access to the data and expertise needed to manage the disease. And neither does the public.

The Importance of Leading and Lagging Indicators for Ongoing Monitoring of COVID-19 in Hawaii
While it likely makes sense to most of us that these indicators measure different components of COVID-19 management – i.e. new cases, daily test rates, hospitalizations, etc. – it might be more difficult to understand how they all fit together, and why it is important to have a balance of indicators that represent the range of relevant factors for managing COVID-19 locally. One important frame to consider is distinguishing where data points fall along the continuum of leading to lagging indicators.

Hawaii Appleseed's Gavin Thornton Discusses $100 Million CARES Act Housing Support for Hawaii's Families
Gavin Thornton, Executive Director of the Hawaii Appleseed Center for Law and Economic Justice, discusses recent legislation passed that will provide $100 million of CARES Act funds to folks in need of rental and mortgage support, and why this assistance is necessary to shield the state from even greater costs in the future.

Dr. Thomas Lee, HI-EMA's Lead Modeler & Forecaster, Discusses Reopening Hawaii to Travel and More
Dr. Thomas Lee, Assistant Professor of Epidemiology at the University of Hawaii at Manoa, also an US Army Medical Officer from the 1984th US Army Hospital Pacific, 9th Mission Support Command, currently serving as lead modeler and forecaster for Hawaii’s Emergency Management Agency (HI-EMA) COVID-19 Emergency Response Team, discussed how he applies modeling to forecast and advise policymakers in their decisions, the potential and efficacy of testing and screening of inbound travelers, a basic explanation of “R naught,” and more.

Testing Testing 1-2-3
Respondents of our survey perceive that access to testing is insufficient. Many survey participants expressed frustration with the inability to meet the criteria for testing, despite showing symptoms or other factors they believe warrant COVID-19 testing. In addition, home test kits were mentioned numerous times as one preferred method to ensure greater access to adequate testing.
The Good, The Bad, and Social Distancing in Hawaii
During times of crisis, the vulnerable are at even greater risk of becoming casualties of fast moving events. In Hawaii and throughout the nation, we are beginning to see how the current pandemic is overwhelming seniors, those living in poverty, those living on the edge of poverty, and the homeless. They are the most vulnerable in these times. And while they may be overwhelmed, in Hawaii, they are never left behind. That is not what we do nor who we are.
Local Expert-Driven COVID-19 Models for Hawaii Are Long Overdue
We learned the hard way that modeling COVID-19 forecasts is not one-size-fits-all. Recently, we wrote about the advantages of the University of Washington IHME model for understanding peak hospital demand in Hawaii, only to shortly thereafter advise caution in interpreting the model because the projected hospital capacity peak had suddenly shifted by three weeks [link]. A closer inspection of the model revealed problematic assumptions, and underscored a real vulnerability for Hawaii in not having a valid local model.
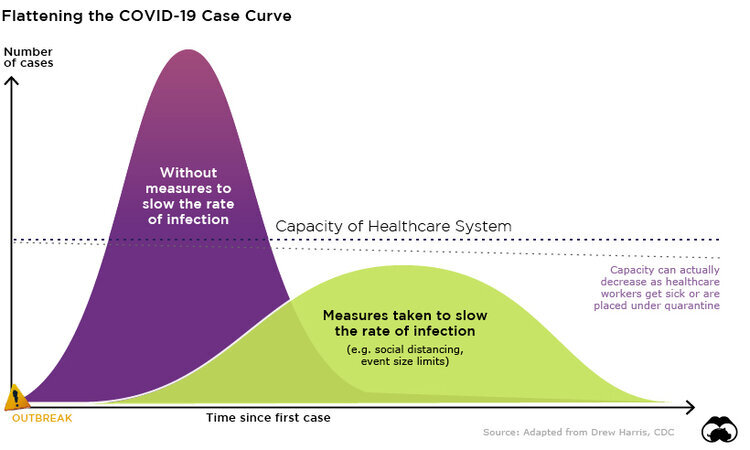
Understanding COVID-19 Transmission in Hawaii
To help illustrate the role of social distancing measures in preventing the spread of COVID-19, we have been working to adapt current transmission models for Hawaii… you can see how existing mitigation efforts are projected to influence the spread of the virus, as compared to no action and more aggressive measures… These forecasts were generated using an accessible modeling tool created by researchers at the University of Basel in Switzerland. This model is updated continuously as new information about COVID-19 becomes available.
